Git 5 - Les pipelines avec Gitlab CI
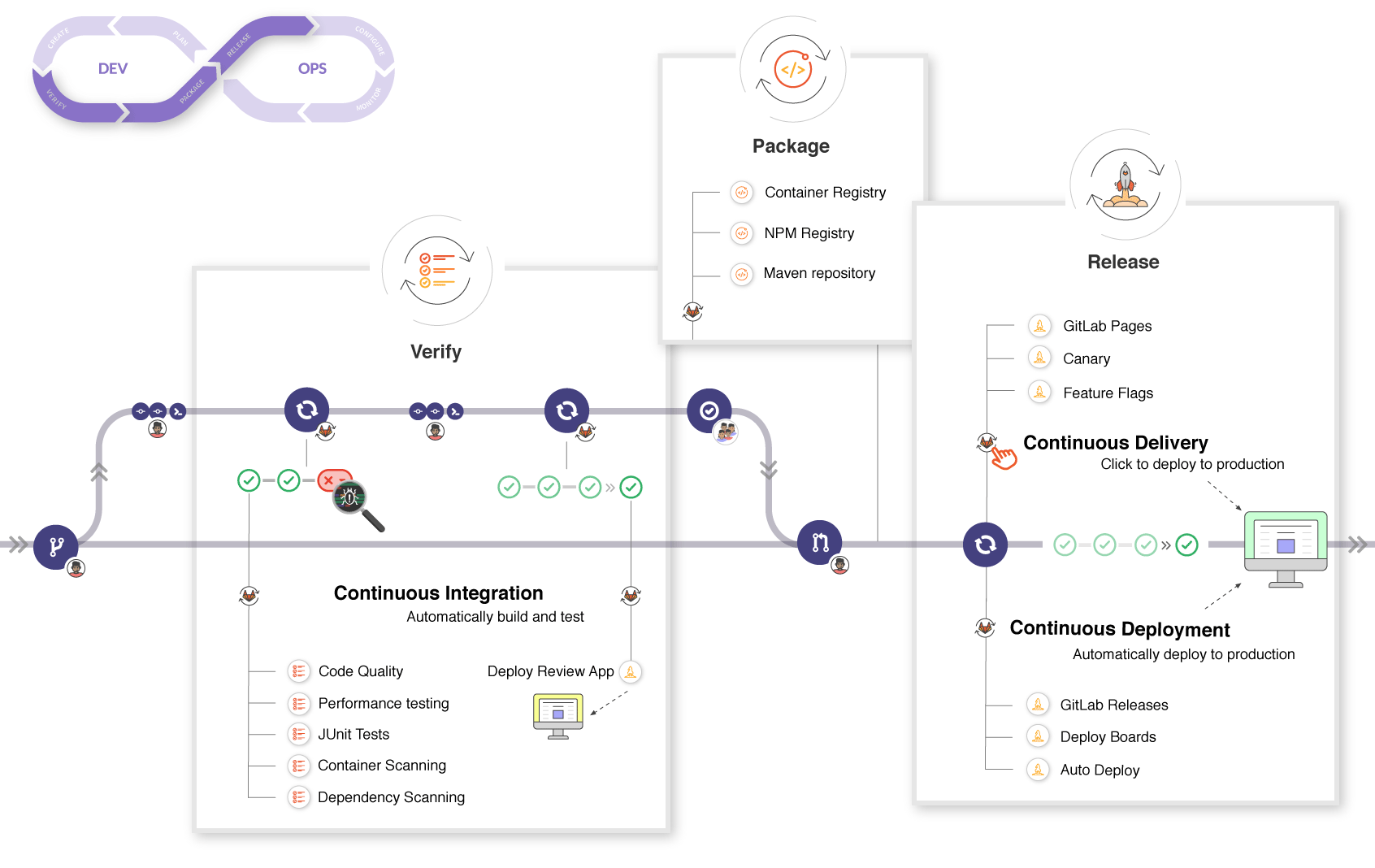
La CI/CD
(intégration continue et déploiement continu)
-
Accélérer la livraison des nouvelles versions du logiciel.
-
Des tests systématiques et automatisés pour ne pas se reposer sur la vérification humaine.
-
Un déploiement progressif en parallèle (Blue/Green) pour pouvoir automatiser le Rollback et être serein.
-
A chaque étape le code passe dans un Pipeline de validation automatique.
La CI/CD fait partie de l’approche DevOps dont fait aussi partie les concepts de cloud (Infrastructure-as-a-Service, IaaS), d’Infrastructure-as-Code et les conteneurs.
Le Cloud (plus précisément : Infrastructure-as-a-Service, ou IaaS)
Plutôt que d'installer manuellement de nouveaux serveurs linux pour faire tourner des logiciels on peut utiliser des outils pour faire apparaître de nouveaux serveurs à la demande.
Du coup on peut agrandir sans effort l’infrastructure de production pour délivrer une nouvelle version
C’est ce qu’on appelle le IaaS (Infrastructure as a service)
Cloud et API
Dans le cloud, à la demande signifie que les vendeurs de cloud fournissent une API (REST généralement) Pour contrôler leur infrastructure.
- Une API est un ensemble de fonctions qu’on peut appeler en codant.
- Une API REST (assez simple et très populaire depuis) est une API qui permet de discuter sur le web avec des informations décrite dans le format JSON.
Exemple pour Scaleway: https://developer.scaleway.com/
Infrastructure As Code
Avantages :
-
On peut multiplier les machines (une machine ou 100 machines identiques c’est pareil).
-
Git ! gérer les version de l’infrastructure et collaborer facilement comme avec du code.
-
Tests fonctionnels (pour éviter les régressions/bugs)
-
Pas de surprise = possibilité d’agrandir les clusters sans soucis !
Les conteneurs
- La nature facile à déployer des conteneurs et l’intégration du principe d’Infrastructure-as-Code les rend indispensable dans de la CI/CD (intégration continue et déploiement continu).
- Les principaux outils de CI sont Gitlab, Jenkins, Github Actions, Travis CI…
- Gitlab propose par défaut des runners préconfigurés qui utilisent des conteneurs Docker et tournent en général dans un cluster Kubernetes.
- Gitlab propose aussi un registry d’images Docker, privé ou public, par projet.
Ressources
Essentiel :
Get started with GitLab CI/CD : https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/quick_start/
La syntaxe Gitlab CI
Documentation de référence de .gitlab-ci.yml : https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/yaml/
Exemples
Exemple de pipeline :
build-job:
stage: build
script:
- echo "Hello, $GITLAB_USER_LOGIN!"
test-job1:
stage: test
script:
- echo "This job tests something"
test-job2:
stage: test
script:
- echo "This job tests something, but takes more time than test-job1."
- echo "After the echo commands complete, it runs the sleep command for 20 seconds"
- echo "which simulates a test that runs 20 seconds longer than test-job1"
- sleep 20
deploy-prod:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "This job deploys something from the $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH branch."
Exemple avec du code Ruby :
stages:
- build
- test
build-code-job:
stage: build
script:
- echo "Check the ruby version, then build some Ruby project files:"
- ruby -v
- rake
test-code-job1:
stage: test
script:
- echo "If the files are built successfully, test some files with one command:"
- rake test1
test-code-job2:
stage: test
script:
- echo "If the files are built successfully, test other files with a different command:"
- rake test2
Exemple réaliste avec Maven :
# Build JAVA applications using Apache Maven (http://maven.apache.org)
# For docker image tags see https://hub.docker.com/_/maven/
#
# For general lifecycle information see https://maven.apache.org/guides/introduction/introduction-to-the-lifecycle.html
# This template will build and test your projects
# * Caches downloaded dependencies and plugins between invocation.
# * Verify but don't deploy merge requests.
# * Deploy built artifacts from master branch only.
variables:
# This will suppress any download for dependencies and plugins or upload messages which would clutter the console log.
# `showDateTime` will show the passed time in milliseconds. You need to specify `--batch-mode` to make this work.
MAVEN_OPTS: "-Dhttps.protocols=TLSv1.2 -Dmaven.repo.local=$CI_PROJECT_DIR/.m2/repository -Dorg.slf4j.simpleLogger.log.org.apache.maven.cli.transfer.Slf4jMavenTransferListener=WARN -Dorg.slf4j.simpleLogger.showDateTime=true -Djava.awt.headless=true"
# As of Maven 3.3.0 instead of this you may define these options in `.mvn/maven.config` so the same config is used
# when running from the command line.
# `installAtEnd` and `deployAtEnd` are only effective with recent version of the corresponding plugins.
MAVEN_CLI_OPTS: "--batch-mode --errors --fail-at-end --show-version -DinstallAtEnd=true -DdeployAtEnd=true"
# This template uses jdk8 for verifying and deploying images
image: maven:3.3.9-jdk-8
# Cache downloaded dependencies and plugins between builds.
# To keep cache across branches add 'key: "$CI_JOB_NAME"'
cache:
paths:
- .m2/repository
# For merge requests do not `deploy` but only run `verify`.
# See https://maven.apache.org/guides/introduction/introduction-to-the-lifecycle.html
.verify: &verify
stage: test
script:
- 'mvn $MAVEN_CLI_OPTS verify'
except:
variables:
- $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH
# Verify merge requests using JDK8
verify:jdk8:
<<: *verify
# To deploy packages from CI, create a ci_settings.xml file
# For deploying packages to GitLab's Maven Repository: See https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/packages/maven_repository/index.html#create-maven-packages-with-gitlab-cicd for more details.
# Please note: The GitLab Maven Repository is currently only available in GitLab Premium / Ultimate.
# For `master` branch run `mvn deploy` automatically.
deploy:jdk8:
stage: deploy
script:
- if [ ! -f ci_settings.xml ];
then echo "CI settings missing\! If deploying to GitLab Maven Repository, please see https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/packages/maven_repository/index.html#create-maven-packages-with-gitlab-cicd for instructions.";
fi
- 'mvn $MAVEN_CLI_OPTS deploy -s ci_settings.xml'
only:
variables:
- $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH